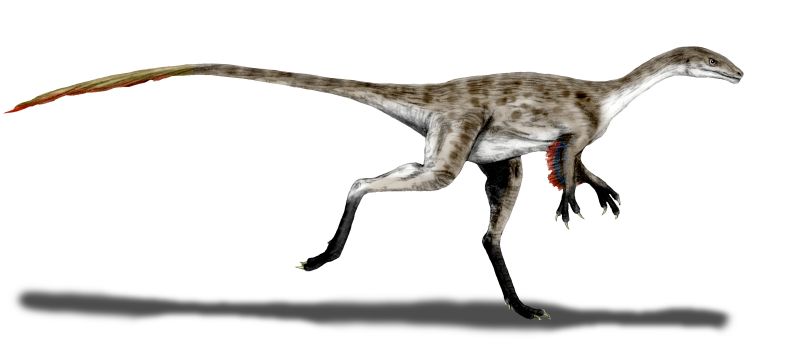
Coelurus

Description
Source: Wikipédia
Cœlurus (« queue creuse ») est un genre éteint de dinosaures coeluridés ayant vécu au Kimméridgien (Jurassique supérieur), il y a environ entre 155 et 152 Ma (millions d'années),.
Information(s)
Source: The Paleobiology Database
- Attibution: Marsh 18797814
- Statut: Valide
- Nom commun: A queue creuse
- Environnement de découverte: terrestrial
- Mode de vie: terrestrial
- Mode de locomotion: actively mobile
- Vision: ?
- Alimentation: carnivore
- Mode de reprodution: oviparous, dispersal=direct/internal,mobile
- Classification: Coelurosauria >> Tetanurae >> Averostra >> Neotheropoda >> Theropoda >> Dinosauria
- Période: ?
- Espèce(s):
- Coelurus agilis (Synonyme objectif de Coelurus fragilis)12248
- Coelurus fragilis (Valide)7814
- Coelurus gracilis (nomen dubium, voir Coelurus)7834
- Coelurus longicollis (Synonyme subjectif de Coelophysis bauri)9090
- Specimen(s):
- Coelurus agilis objective synonym of Coelurus fragilis: holotype YPM 2010 - femur, ulna, ulna, radius, humerus
- Détail des Spécimens
- Autre(s) Taxon(s) trouvés dans la litterature:
- Coelurus bauri recombined as Coelophysis bauri
- Découverte(s): 20 occcurrences
Ouvrir - Fermer - Historique des modifications:
Pas de modification récente.
Publication(s)
La base comprend 17 publication(s).
Source: The Paleobiology Database
- ↑1 2 3 O. C. Marsh. 1879. Notice of new Jurassic reptiles. The American Journal of Science and Arts, series 3 18:501–505 (https://doi.org/10.2475/ajs.s3-18.108.501)
- ↑1 2 O. C. Marsh. 1884. Principal characters of American Jurassic dinosaurs. Part VIII. The order Theropoda. The American Journal of Science, series 3 27:329-340 (https://doi.org/10.2475/ajs.s3-27.160.329)
- ↑1 2 O. C. Marsh. 1888. Notice of a new genus of Sauropoda and other new dinosaurs from the Potomac Formation. American Journal of Science 35:89-94 (https://doi.org/10.2475/ajs.s3-35.205.89)
- ↑1 2 3 E. D. Cope. 1887. The dinosaurian genus Coelurus. American Naturalist 21:367-369
- ↑1 2 C.-C. Young. 1942. Fossil vertebrates from Kuangyuan, N. Szechuan, China. Bulletin of the Geological Society of China 22(-34):293-309 (https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-6724.1942.mp223-4016.x)
- ↑1 C. -C. Young, M. N. Bien, and T. H. Mi. 1943. Some geologic problems of the Tsinling. Bulletin of the Geological Society of China 23(1–2):15-34 (https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1755-6724.1943.mp231-2002.x)
- ↑1 X. He. 1984. The Vertebrate Fossils of Sichuan. Sichuan Scientific and Technological Publishing House, Chengdu
- ↑1 C. W. Gilmore. 1914. Osteology of the armored Dinosauria in the United States National Museum, with special reference to the genus Stegosaurus. United States National Museum Bulletin 89:1-136 (https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.63658)
- ↑1 W. E. Miller, J. L. Baer, and K. L. Stadtman, B. B. Britt. 1991. The Dry Mesa Dinosaur Quarry, Mesa County, Colorado. Guidebook for Dinosaur Quarries and Tracksites Tour, Western Colorado and Eastern Utah
- ↑1 T. R. Lipka. 1998. The affinities of the enigmatic theropods of the Arundel Clay facies (Aptian), Potomac Formation, Atlantic Coastal Plain of Maryland. Lower and Middle Cretaceous Terrestrial Ecosystems; New Mexico Museum of Natural History and Science Bulletin 14:229-234
- ↑1 J. Bertog, D. L. Jeffery, and K. Coode, W. B. Hester, R. R. Robinson, J. Bishop. 2014. Taphonomic patterns of a dinosaur accumulation in a lacustrine delta system in the Jurassic Morrison Formation, San Rafael Swell, Utah, USA. Palaeontologia Electronica 17(3):36A:1-19 (https://doi.org/10.26879/372)
- ↑1 K. Carpenter, C. A. Miles, and J. H. Ostrom, K. C. Cloward. 2005. Redescription of the small maniraptoran theropods Ornitholestes and Coelurus from the Upper Jurassic Morrison Formation of Wyoming. The Carnivorous Dinosaurs. Indiana University Press, Bloomington
- ↑1 2 M. V. Connely. 2002. Stratigraphy and Paleoecology of the Morrison Formation, Como Bluff, Wyoming
- ↑1 C. W. Gilmore. 1909. A new rhynchocephalian reptile from the Jurassic of Wyoming, with notes on the fauna of "Quarry 9". Proceedings of the United States National Museum 37(1698):35-42 (https://doi.org/10.5479/si.00963801.37-1698.35)
- ↑1 J. H. Ostrom and J. S. McIntosh. 1999. Marsh's Dinosaurs: The Collections from Como Bluff. Yale University Press, New Haven
- ↑1 J. H. Ostrom. 1980. Coelurus and Ornitholestes: are they the same?. Aspects of Vertebrate History: Essays in Honor of Edwin Harris Colbert
- ↑1 H. Galiano and R. Albersdörfer. 2010. A New Basal Diplodocoid Species, Amphicoelias brontodiplodocus from the Morrison Formation, Big Horn Basin, Wyoming, with Taxonomic Reevaluation of Diplodocus, Apatosaurus, Barosaurus and Other Genera. Dinosauria International (Ten Sleep, WY) Report for September 2010
Galerie d'images
Source: Wikimédia